Brand advocate or Influencer: Are you driving on the streets of loyalty?
In many seminars there is a common opinion: Brand advocates and social media influencers are cast in the same mold. They are not! They are completely different kind of personalities. However, this does not say that they cannot change their roles from brands to brands. Still, the question is whether they might suddenly become both in the future: influencer and advocate. We have shared our thoughts a while ago…
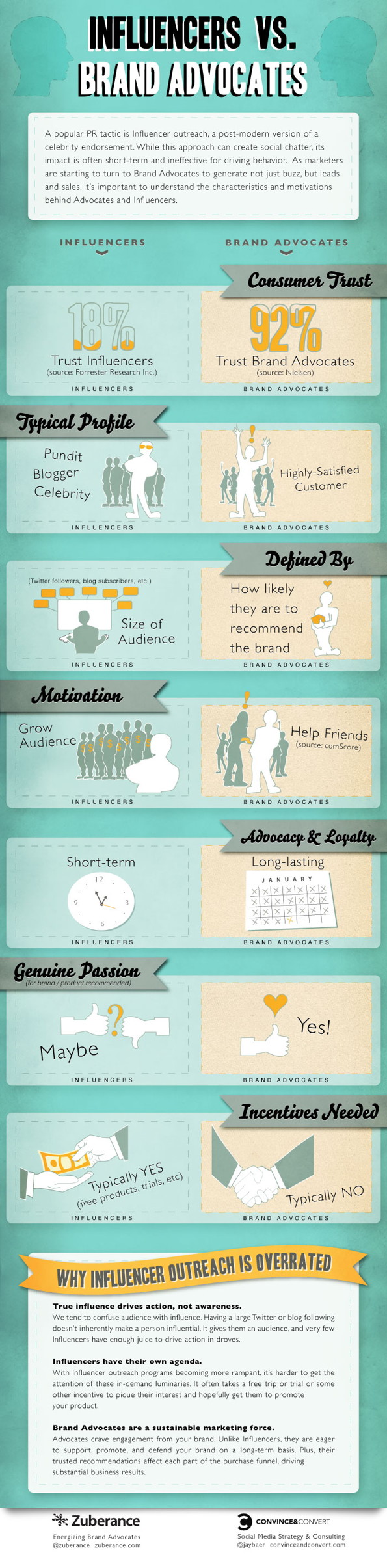
So, how can advocates and influencers be defined (backed up by an infographic from Zuberance and Convince and Convert below)?
Advocates are customers of brands. They are not heading for money or incentives that a brand or company might pay them for going out and holding up signs “I love this brand!”. In fact, it is just the other way round: They often pay brands more than they have to. Personal persuasion, individual enthusiasm and emotions the brand creates lead them to recommend products to their fellows, friends and fans without any reward. These people are just happy with a brand or product. The brand has satisfied their needs and desires which let’s them engage in discussion they are not really part of. These people are actually looking for engagement around the brand and might even start conversations that foster new brand approaches, or even design new product concepts.
Influencers were -well, in the days before social media- people that were wearing logos on shirts, were used as testimonials or stood in front of a camera and talked about a product or service as a client case (things they often had no clue about). Nowadays, there is a new type of influencers coming up that gets paid by blogging or social media monetization platforms, and in the end from brands and companies. These bloggers or social media active people write or talk online about brands predominantly as they get paid for promoting the brand or product. In most cases, these bloggers have a great community of people that build an attractive audience (whether as of reach or relevance) for the brand or company – maybe simply to increase the influencer base or to spread the word (word-of-mouth) around the brand.
The main difference between the two?
Advocacy goes deeper. Advocacy is emotion-driven. Advocacy is loyalty. Loyalty is commitment. Loyalty is passion. Loyalty let’s forget the rules of logic, of facts, of the rational. Advocates drive on the streets of loyalty and breath it’s air.
A recent study by Ogilvy claims that social media influencers don’t use these streets of advocacy and passion, the streets of the brands they follow. The study makes cleat that most “advocates” -in the above definition probably more influencers- mentioned product features and not emotions. Only 9% of brands were lucky to facing greater than 50% of brand advocacy. And, “advocacy” posts constituted only 15% of social mentions.
Click on the button to load the content from www.slideshare.net.
Marketers need to understand the value of brand advocacy. Advocats are the elite of your brand fans, and marketers that do not identify those advocates will leave out the opportunity to spend marketing budgets more wisely:
“Brands that do not generate substantial advocacy will need to pay more for reach and consequently have costs substantially higher than those brands that drive advocacy… this advantage could make the difference between a company with outstanding shareholder returns and one that fails to perform.”
Hey marketers, just think about yourself: Would you tattoo yourself with the brand you love, like i.e. many Harley Davidson fans? Let us know…







 Many brand managers ask themselves (and us in seminars) how a shitstorm begins. We most often tell them that many shitstorms are not real business problem but more a “verbal foul-mouthed fart” as we called it some weeks ago in one of the courses at the Executive Campus of the University of St. Gallen.
Many brand managers ask themselves (and us in seminars) how a shitstorm begins. We most often tell them that many shitstorms are not real business problem but more a “verbal foul-mouthed fart” as we called it some weeks ago in one of the courses at the Executive Campus of the University of St. Gallen.
